RNIB and Oxford University project wins Google’s UK Impact Challenge
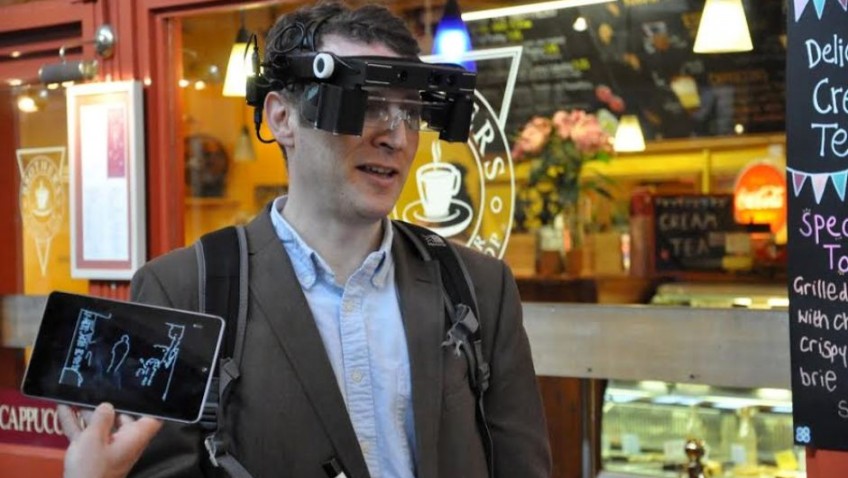
Smart glasses which help blind and partially sighted people to ‘see’ have been chosen by the public as one of the winners at the final of the Google Impact Challenge 2014.
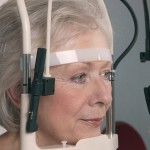
The Royal National Institute of Blind People (RNIB) and Oxford University have worked together to develop the high-tech smart glasses that maximize what remaining vision a person has. Many people who tried the glasses were able to see shapes and obstacles for the first time in years.
The project was named as the winner of the public vote at today’s grand finale event. For the past two weeks people have voted for their favourite project and the smart glasses captured the public’s imagination, gaining the highest number of votes.
Neil Heslop, Managing Director RNIB Solutions, said: “We are absolutely delighted to be the winner of the Google Impact Challenge 2014 public vote. Thank you so much to everyone who voted for the smart glasses.
“These glasses have the potential to transform the way blind and partially sighted people can go about their everyday lives. One gentleman with sight loss who tried the glasses reacted with ‘wow, I can see your face’.
“With this funding we can now increase the number of pairs of glasses in production and set up bigger user testing trials. We want more people to try them, to see the difference they make and let us know how we can make them even better.”
The glasses work by capturing images of the world with a 3D camera. This information is used to separate out nearby shapes and objects and highlight them clearly on the inside of small transparent displays. The displays form part of the lenses of the glasses, allowing people to use their own vision as much as possible.
The £500,000 funding will enable RNIB and Oxford University to create 100 pairs of smart glasses and test them with 1,000 people. This will be the first large-scale test of smart glasses and augmented reality for sight enhancement anywhere in the world.